Say Hello to the oVirt Engine Virtual Appliance
One of the things on the list for oVirt 3.5 was the oVirt Virtual
Appliance. Huh, what’s
that? You might ask. Well, imagine a cloud image with oVirt Engine 3.5
and it’s dependencies pre-installed, and a sane default answer file for
ovirt-engine-setup. All of this delivered in an OVA file. The
intention is to get you a running oVirt Engine without much hassle.
Furthermore this appliance can be used in conjunction with the Self Hosted Engine feature, and the upcoming oVirt Node Hosted Engine plugin (note the Node within).
Just as a reminder to myself: Hosted Engine is a feature where a VM containing the oVirt Engine instance is managed by itself.
As you can find more informations about the oVirt Hosted Engine and oVirt Node Hosted Engine elsewhere, let me just drop a couple of words on the appliance.
The appliance is based on the Fedora 19 cloud images, with some
modifications and oVirt Engine packages pre-installed. An answer file
can be used as a starting point for engine-setup.
Quick Guide
Build Download the appliance yourself
# Get the sources
$ git clone git://gerrit.ovirt.org/ovirt-appliance
$ cd ovirt-appliance
$ git submodule update --init
$ cd engine-appliance
# To only build the `.raw` image use:
$ make ovirt-appliance-fedora.raw
# And run the image:
$ qemu-kvm -snapshot -m 4096 -smp 4 -hda ovirt-appliance-fedora.raw
Inside the VM:
- Wait a bit
- Finish the
initial-setup(set a root password and optionally add a user)
and run:
$ engine-setup --config-append=ovirt-engine-answers
Building the virtual appliance
To build the appliance you need three ingredients:
- The appliance kickstarts (kept in the ovirt-appliance repo)
- A Fedora 19 boot.iso (or the netinstall iso)
loraxandpykickstartinstalled
The build process can then be initiated by running:
$ yum install lorax pykickstart
$ git clone git://gerrit.ovirt.org/ovirt-appliance
$ cd ovirt-appliance
$ git submodule update --init
$ cd engine-appliance
# Build the .ova
$ make
# Or: To only build the `.raw` image (without sparsification/sysprep) use:
$ make ovirt-appliance-fedora.raw
The .ova build will actually go through the following steps:
- Create a kickstart from the provided template
- Pass the boot iso and kickstart to
livemedia-creator(part oflorax) - sysprep, resize, sparsify and convert the intermediate image to OVA
The .ova file now contains some metadata and the qcow2 image, to
extarct the image run:
$ mkdir out ; cd out
$ tar xf ../ovirt-appliance-fedora.ova
# Run the image:
$ qemu-kvm -snapshot -m 4096 -smp 4 -hda images/*/!(*.meta)
Running the virtual appliance
Once the image is build - an image called ovirt-appliance-fedora.ova
should be in your working directory - you can point
hosted-engine-setup to it, which will use it for the initial VM. If
you want to try the imagine with qemu (or libvirt), just use the .raw
image (also available in the current workingdir) and something like:
$ qemu-kvm -snapshot -m 4096 -smp 4 -hda ovirt-appliance-fedora.raw
Once you boot into the image, the initial-setup dialog will pop-up to
guide you through some initial steps.
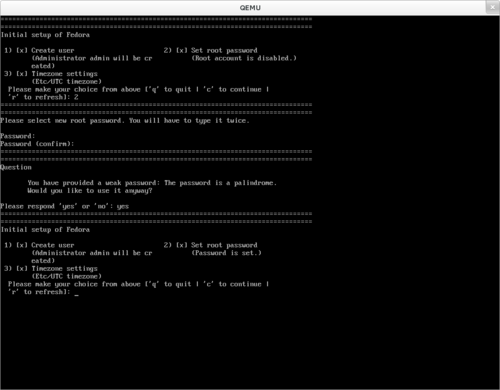
Finishing the ovirt-engine-setup
Once you finished the initial-setup (which should be self describing),
login as root and run:
$ engine-setup --config-append=ovirt-engine-answers
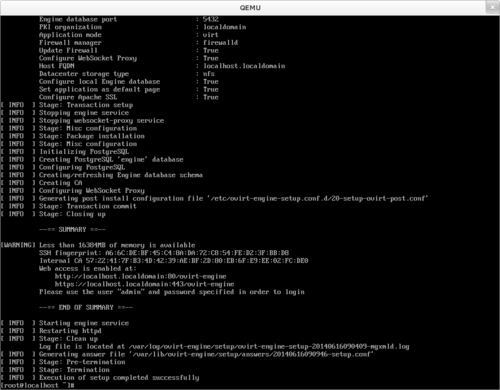
Comments on some design decisions
Why Fedora and why 19? Because oVirt Engine runs fine on Fedora 19. Also Fedora provides a nice set of cloud images (kickstarts) from which the oVirt Engine appliance inherits, this eases the maintenance. Fedora 20 is not used because Engine did not support it when the development of the appliance started.
Why not CentOS? We started with Fedora 19, because the cloud images where available, the plan is to either adapt them to CentOS, or look if they’ve also got cloud image kickstarts from which we could inherit.
Why initial-setup? Another reason for using Fedora 19 was, that
anaconda could be leveraged to run the inital-setup. The
initial-setup is responsible to ask the user some questions (what root
password, what timezone, and if an additional user should be created).
cloud-init could not be used, because cloud-init requires some kind
of management instance at boot time (like oVirt or OpenStack) to get
configured. But this isn’t the case with the virtual appliance, because
the appliance will only become the Engine.
A FutureFeature could be to add another spoke to the initial-setup
where the remaining questions for the engine-setup are asked, that way
a user is actually guided through the setup, and does not need to
manually trigger the engine-setup after login.
Less maintenance!? In general the ovirt-appliance-fedora.ks
inherits from the fedora-spin-kickstarts/fedora-cloud-base.ks file. We
also try hard to not diverge to much from the upstream configuration.
But some modifications are applied to the final (post-ksflatten)
kickstart, to change some defaults which are currently set in the
fedora-cloud-base.ks.
In detail we do the following: * Don’t blacklist any package - To
prevent missing dependencies * Disable text installation - This does
not work with livemedia-creator * Change the partition (rootfs) size
to 4GB * Generalize network activation - To be independent of nick
names * Ignore missing packages - Because the cloud ks uses Fedora 20
package names * Do not explicitly set the default target * Remove
disablement of initial-setup - Because we use it * Remove dummy user
game - Not needed because initial-setup is used
Take a look at the Makefile for the exact informations.
Where is the UI? The appliance comes without a desktop environment. There is no hard need for it (some other host with an OS can be used to access Engine’s web-ui) and it keeps the image small.
If you want to add a desktop environment, you are free to do so, by
using yum.
Next steps
This is the first shot of this appliance. Let’s see how it turns out. Some integration tests with the oVirt Node Hosted Engine plugin are pending. I expect some more cleanup and fixes, before it’s ready for the oVirt 3.5 TestDays.
Open items include:
- Heavy testing
- …
So feel enlighted to try out the ready to use image or build the
appliance
yourself.
Please provide feedback and questions to the users@ovirt.org
mailinglist.
::: {#footer} [ June 16th, 2014 11:16am ]{#timestamp} [ovirt]{.tag} [appliance]{.tag} [engine]{.tag} [node]{.tag} [19]{.tag} [libguestfs]{.tag} [libvirt]{.tag} [qemu]{.tag} [lorax]{.tag} [ova]{.tag} [virtual]{.tag} [hosted-engine]{.tag} [fedora]{.tag} :::
 {width=”500”
height=”375”}
{width=”500”
height=”375”}